Optical Components: Optical lenses, Filters, Laser optics
 |
Egismos optics offer a wide range of optical components and electro-optical solutions, including spherical lenses, aspheric lenses, collimating lenses, laser collimators, coupling lenses, fiber coupling lens, laser optics (laser collimating lens, laser coupling lens, laser line generator lenses...), optical filters (UV filters, infrared filters, bandpass filters...), and diffractive optical elements (DOE). We also offer customization services and provide optical design for any kind of application. Please contact us for more inquiries about our optical devices. |
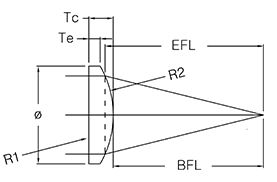
Egismos proposes a large offer of off-the-shelf optical components, which includes an extensive selection of optical lenses, such as spherical lenses. Many of our optical lenses are provided with a variety of coating options for the Ultraviolet (UV), visible, or Infrared (IR) spectrum.
The spherical lenses such as the Plano-Convex (PX) or Double-Convex (DX) lenses enable laser light to focus to a single point; while the Plano-Concave (PV) or Double-Concave (DV) lenses will allow the light traveling through the lens to diverge.
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Example: O | 1 | CO | 7 | 8.9 | A |
| Product Code of Optics | Number of Lenses | Lens Type | Lens Diameter (mm) | EFL or NA | Material & Process |
| O: Optics | 1: singlet | DX,DV: double convex, concave | 10: 10mm | EFL: effective focal length | A: aspheric glass lenses |
| 2: glue coupling lens or doublet lenses | PX,PV: plano convex,concave | 25: 25mm | NA: numerical aperture | G: spheric glass lenses | |
| 3: triplet lens or three lenses set | H: hybrid lenses | ||||
| 4: four lenses set | P: plastic lenses |
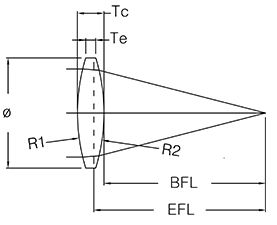
Egismos aspheric lenses are used as laser collimators (or laser collimating lenses), laser coupling lenses or fiber coupling lenses.
A collimating lens helps a divergent light traveling through the lens to converge as a collimated beam (a non-divergent light). This property is usually used for laser diode collimation or light collimating applications. The coupling lenses are mostly used for coupling lasers to fibers, as a divergent light will focus to a point into the fiber (for example: like laser diode to fiber coupling or fiber to fiber coupling).
We also provide customized aspheric lenses for specific applications; if you have such requirements don't hesitate to contact us at:sales@egismos.com
|
|
|
|
| Example: O | 1 | CO | 7 | 8.9 | A |
| Product Code of Optics | Number of Lenses | Lens Type | Lens Diameter (mm) | EFL or NA or angle | Material & Process |
| O: Optics | 1: singlet | CO: collimator | 2.4: 2.4mm | EFL: effective focal length | A: aspheric glass lenses |
| 2: doublet lens or two elements system | CP: coupling lens | 6.3: 6.3mm | NA: numerical aperture | G: spheric glass lenses | |
| 3: triplet lens or three elements system | LG: Line Generator | 6.5: 6.5mm | H: hybrid lenses | ||
| 4: four elements system | CG: Cross Line Generator | 8: 8mm | 100: 100 degrees | P: plastic lenses | |
| 5: five elements system | RO: Rod Lens | 360: 360 degrees | |||
| E: Element | CY: Cylindrical Lens |
Many optical systems require filters in order to work within a specific range of wavelengths, and Egismos has therefore developed a comprehensive selection of standard as well as custom filters for any requirement.
Whether it is for transmitting specific wavelengths of a light source or blocking them, Egismos UV pass filters, UV cut filters, Infrared pass filters, Infrared cut filters or bandpass filters are optimized for all kinds of applications.
|
|
|
|
| Product Code of Optics | Filter Code | Central Wavelength | Size | FWHM |
| OF: Optical Filter | BP: Bandpass Filter IP: IR Pass IC: IR Cut UP: UV Pass UC: UV Cut |
400 650 700 808 1050 . . . |
Diameter R1: 12.5mm R2: 25mm RX: Custom
Square m5: 5*5mm c1: 10*10mm c2: 20*20mm d1: 100*100mm SX: custom |
N: Narrow band = FWHM<10nm
S: Standard band=10<FWHM<40nm B: Broadband= 40<FWHM<70nm E: Extra Broadband= FWHM>70nm
|
| OW: Window Glass | Feature | Size | Thickness | Material |
| AR: Anti Reflection coating NC: No Coating IP: IR Pass IC: IR Cut UP: UV Pass UC: UV Cut |
Diameter R08: 8mm Square S05: 5*5mm |
03: 3mm | S: Sapphire Q: Quartz O: Optical Glass P: Plastic |
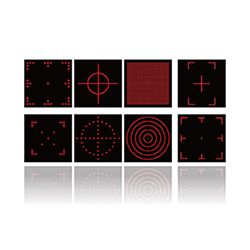
Diffractive Optical Elements (DOE) are nowadays the best solutions for laser systems to generate a wide variety of patterns.
DOEs can reach very thin thicknesses, high compactness and very light weight compared to other traditional optical components. Moreover, the use of DOE enables the projection of highly straight, uniform and precise lines of laser patterns. Egismos now provides various kinds of high quality DOEs with high resolution, and also designs customized DOE upon inquiries.
For industrial, medical or consumers applications, the most common laser patterns include : laser cross, laser target, laser matrix, laser grid.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Example: O | DE | R | 43 | L | 1 | G |
| Product Code of Optics | Lens type | Element Shape | Lens diameter | Pattern | NA | Material |
| O: Optics | DE: DOE - Diffractive Optics Element | S:Square | 4: 4x3 | L: Line | DOE Part Number | G: Glass |
| R: Rectangular | 6: 6x6 | R: Round | P:Plastic | |||
| C: Circular | C: Cross | |||||
| M: Matrix | ||||||
| V: View finder | ||||||
| T: Target |
The spherical lenses are the most common type of optics. They comprise at least one surface that is a segment of a ball.
Egismos designs and manufactures standard and custom spherical optics to fit any kind of application.
What is a Spherical Lens
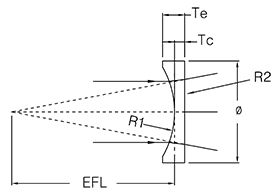
A spherical lens is a lens whose surface is a portion of a sphere. Spherical lenses can be classified into six categories: double convex, plano convex, positive meniscus, negative meniscus, plano concave and double concave lens.
The different types of Spherical Lenses
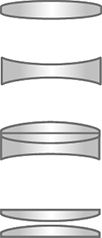 |
Simple Positive Lens - A single piece of optical glass or acrylic with two convex surfaces (curved outward). Designed for low magnification. Simple Negative Lens - A single piece of optical glass or acrylic with two concave surfaces (curved inward). Used in conjunction with positive lenses. Achromatic Lens - A positive simple lens cemented to a negative simple lens.Achromatic lenses are corrected for two colors and produce flatter fields of view at higher powers. Double Lens - Two simple lenses used as a system but not cemented together. This system produces a far superior image than a simple lens. |
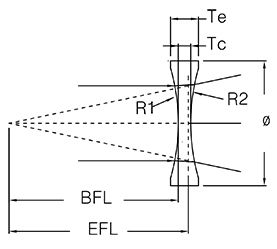
What is the Back Focal Length?
The Back focal length is defined as the distance from the vertex of the last optical surface of one system to its rear focal point along the optical axis. It is also called “working distance”.
What is an Aspherical Lens?
An Aspherical lens is a lens with a special surface which radius of curvature varies with respect to the distance from the optical axis. Its surface can be a slightly modified spherical portion or resulting from a more complex surface function, such as parabolic, elliptic, etc.
Aspheric lenses have one or more optical surfaces of non-constant curvature. They are used to avoid aberrations existing in spherical lens systems, and to reduce the optical systems overall dimensions and weight.
Spherical aberration happens when focusing or collimating light through a spherical surface: all spherical surfaces will produce such spherical aberration regardless of the alignment or the manufacturing errors. Through the adjustment of the parameters of the lens, such as the conic constant and the aspheric coefficients, the aspheric lenses are designed to minimize the spherical aberration.
The correction of aberration using aspheric optical systems also allows the use of fewer optical elements than in spherical systems Aspheric systems.
What is the Numerical Aperture?
The numerical aperture (NA) is the measurement of how large an angle of a light cone is for one optical system to accept incident light or emit transmitted light.
The Numerical Aperture is defined as N.A. = n * sin(θ), where n is the refractive index of the medium wherein the light is propagating and θ is the maximal half-angle of the light entering or exiting the optical system.
The Numerical Aperture is dimensionless.
What is the Divergence Angle?
The divergence angle of a laser beam is the angle measured when a beam expands from its optical axis. A well designed and precisely manufactured collimator lens will convert a divergent laser source into a good collimated beam with the smallest divergence angle possible.
What is a Bandpass filter:
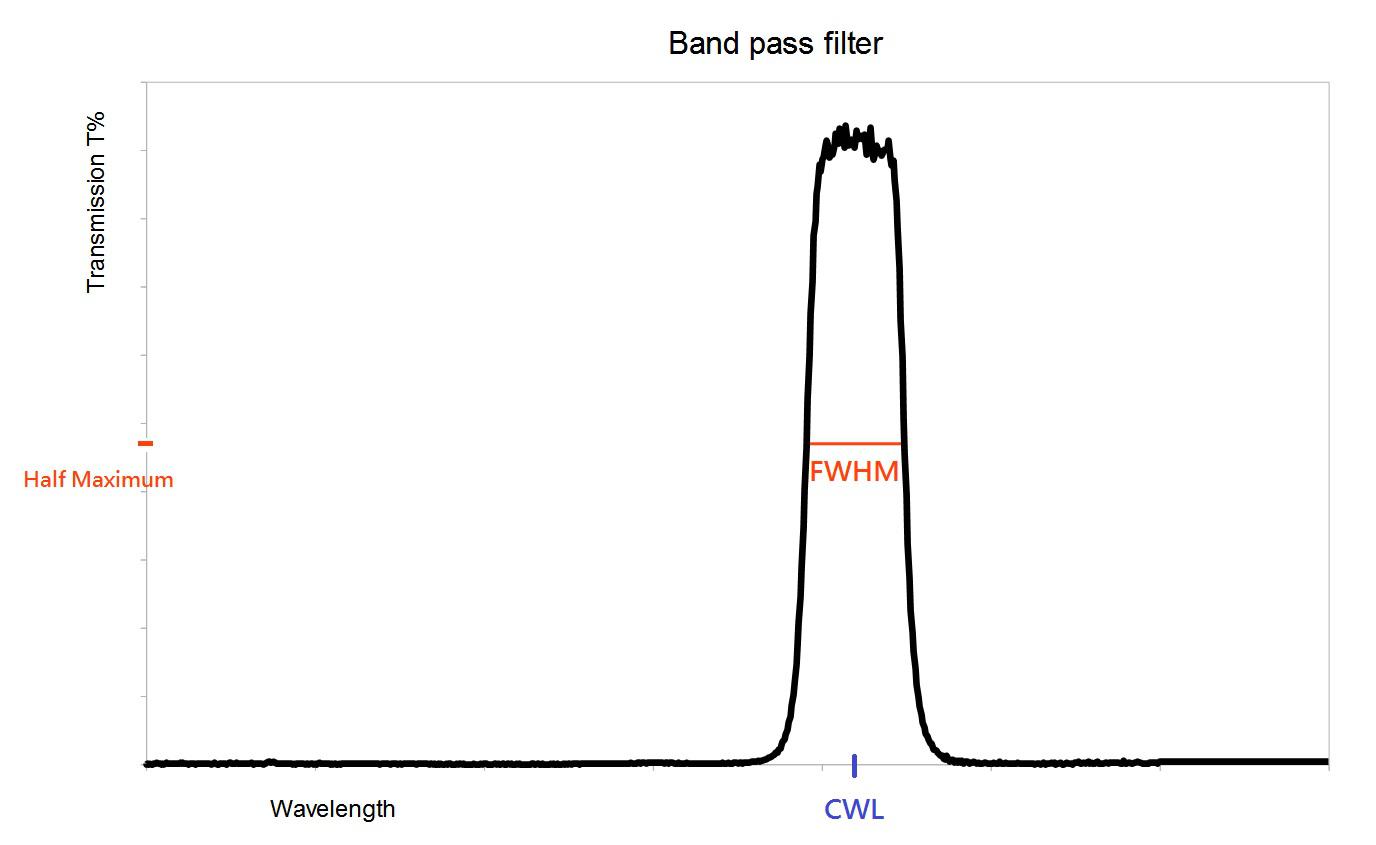
Band pass filters are optical filters which transmit only a specific range of wavelengths of the light spectrum.
They are defined with a Central Wavelength (CWL) which is the center of said transmitted band and a FWHM (Full Width at Half Maximum) which corresponds to the effective width of the transmission band.
What is a cut off filter (UV cut filter or IR cut filter) ?
UV cut off filters are filters designed to stop all wavelengths in the range of the UV spectrum. UV cut filters have a cut off wavelength, which is the wavelength at which the transmission is half of the maximal transmission. Below this cut off wavelength, the ultraviolet wavelengths are blocked and above this cut off wavelength, the visible light is transmitted.
On the other side of the spectrum, IR cut off filters will transmit the visible light and block all wavelengths in the infrared spectrum above their cut off wavelengths.
What is a pass filter (UV pass filter or IR pass filter) ?
UV pass filters are designed to transmit only wavelengths in the ultraviolet spectrum and not the visible spectrum. Each filter has a cut off wavelength (CWL) that defines the limit between the transmitted and the blocked wavelengths. UV filters are a kind of short pass filters, eg: the filter transmit shorter wavelengths and block longer wavelengths according to their CWL.;
On the other side of the spectrum, IR pass filters will transmit only infrared wavelengths and not the visible light. IR pass filters are a kind of long pass filters, eg: the filters transmit longer wavelengths and block shorter ones according to their CWL.
What are Diffractive Optical Elements (DOE)??
Diffractive Optical Elements are elements with micro-structured surfaces that use their surfaces light diffractive properties and Fourier transforms to produce specific patterns.
The micro-structured surface of a Diffractive Optical Element is etched in silica, glass or polymer materials and comprises several layers.
The DOE are used with laser sources to project complex patterns of light, such as laser targets, laser circles, laser matrix.